The UK's Next Interest Rate Decision: What You Need to Know
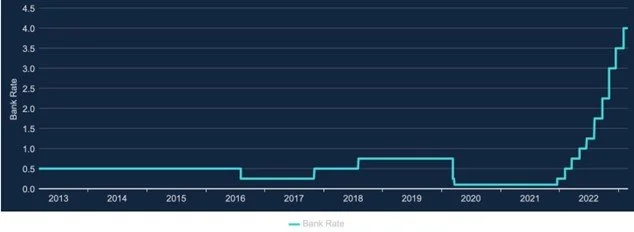
Interest rates play a critical role in the economy and our finances. The Bank of England has raised interest rates from 0.25% to 4% since December 2022, representing a 375 basis-point (bps) increase. Its next decision on March 23, 2023, will be closely watched by economists and individuals alike. In this article, we will explore what interest rates are, how they affect us, and the potential impact of quantitative easing (QE).
What is the Interest Rate?
Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money. When the Bank of England raises interest rates, it makes it more expensive to borrow money, which can slow down spending and investment. On the other hand, when interest rates are lowered, it becomes cheaper to borrow money, which can encourage spending and investment.
The Current Inflation Rate and Target Inflation Rate
Inflation refers to the overall increase in prices of goods and services in an economy over time. It means that, on average, things become more expensive, and the purchasing power of money decreases. Inflation can be caused by various factors, such as an increase in the demand for goods and services, an increase in production costs, or a decrease in the supply of goods and services. Moderate inflation can be beneficial for an economy as it can encourage spending and investment, but high inflation can lead to decreased purchasing power, reduced savings, and decreased investment, which can negatively affect economic growth and stability. To manage inflation, central banks and governments often use interest rates as a tool. Raising interest rates can make borrowing money more expensive, which can slow down spending and investment. This, in turn, can reduce demand for goods and services, which can help to bring down inflation. Therefore, an increase in interest rates can be seen as a measure to combat rising inflation.
Currently, the UK's inflation rate is at 10.1%, well above the Bank of England's target inflation rate of 2%. The Bank of England can use interest rates to combat inflation by making borrowing more expensive and slowing down spending and investment.
What is the Bank of England Saying?
During the 1970s in England, interest rates experienced significant fluctuations due to various economic and political factors. In the early 1970s, inflation began to rise rapidly, which prompted the Bank of England to raise interest rates to curb inflation. However, the oil crisis in 1973 caused oil prices to skyrocket, exacerbating inflation. In 1976, the UK economy faced a financial crisis, and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) demanded that the government raise interest rates even higher to stabilise the economy. The late 1970s saw the introduction of Thatcherism, which aimed to reduce inflation and increase economic growth, resulting in high-interest rates that persisted through the 1980s.
Against this backdrop, after 10 consecutive hikes from December 2021, according to Bank of England Governor Andrew Bailey, interest rates may have peaked as of March 2023. Before taking any additional action, the bank, according to Bailey, would evaluate the effects of tighter policy on the economy. But Bailey also cautioned that should inflationary pressures become entrenched, the Bank would not hesitate to hike rates further from their current 4% level. This is because the Bank is cautious of making the same mistakes it did in the 1970s. At the Bank's most recent meeting of its nine-member monetary policy committee in February, Bailey cast a vote for a quarter-point hike in interest rates, but he made it clear that he was taking a wait-and-see approach. Bailey stated that the incoming data will inform the Bank’s policy decisions regarding the outlook for inflation and the overall economy.
How an Interest Rate Adjustment Will Affect Us
If the Bank of England decides to adjust interest rates, it can affect individuals and the economy.
a. The cost of borrowing rises along with an increase in interest rates. As a result, consumers who have variable-rate loans or credit card debt will have to pay a higher interest rate, raising the cost of borrowing money. Both individuals and corporations may be affected since they may need to pay extra to service their debts.
b. Impact on savings: Higher savings rates could result from an increase in interest rates. Therefore, savers might earn greater interest on their money. Higher savings rates may result in reduced spending and slower economic growth, which can be problematic for people who rely on borrowing to pay for their expenses.
c. Impact on investments: Investments may be impacted by an increase in interest rates. Investors frequently switch their investments from stocks to bonds as interest rates rise, which can affect stock values. On the other hand, when interest rates decline, investors may decide to transfer their funds into equities, which may increase stock prices. Pension funds and other institutional investors as well as individual investors may be impacted by this.
d. Impact on the housing market: Interest rates and inflation may also impact the housing market. The cost of refinancing an existing mortgage or purchasing a home may increase if interest rates rise. This may be very difficult for people who are purchasing their first house or have hefty mortgages. On the other hand, reduced interest rates might make it simpler for people to refinance their mortgages and acquire properties.
e. Impact on the overall economy: A rise in interest rates may affect the economy more broadly. Increased borrowing costs could result in less investment and spending, which would slow economic growth. In contrast, lower interest rates might promote economic expansion since they might encourage consumers to spend more and make more investments.
Adapting to the New Economic Environment
The Bank of England's next interest rate decision on March 23, 2023, will be critical to watch. Understanding how interest rates work and their potential impact on us and the economy can help us make informed financial decisions. When interest rates change, it is important to reassess your financial situation and make informed decisions to adapt to the new economic environment. Some financial decisions that can be made when interest rates change include:
a. Evaluate your debts: A rate increase will boost your interest costs if you have variable-rate loans or credit card debt. To lower your interest costs, think about paying off high-interest debt or combining it with other debt into a fixed-rate loan.
b. Reassess your mortgage: Your monthly payments will go up if you have a variable-rate mortgage. To safeguard yourself against future rate increases, consider refinancing your mortgage to lock in a fixed rate.
c. Review your savings and investments: If interest rates rise, you might want to consider putting money in high-interest savings accounts. Review your portfolio and make any necessary modifications in light of the possibility that investments like stocks and bonds could be impacted by interest rate changes.
d. Consider the impact on your business: If you own a business, interest rate hikes may increase the cost of your borrowing, therefore it's crucial to assess your cash flow and financial situation.
e. Re-evaluate your budget: An increase in interest rates may have an impact on your entire financial condition, so it's critical to review your spending plan and make any required modifications.
Keep in mind that everyone has a different financial condition, so it's crucial to evaluate your situation and make wise financial decisions. Navigating the effects of interest rate increases on your finances may also benefit from seeking the counsel of a financial advisor.
By
Haley Seow